Peppers, particularly hot varieties like chili peppers, are not only a staple in many cuisines around the world but also pack a powerful health punch thanks to their active compound, capsaicin. This article delves into Peppers Knowledge, highlighting how capsaicin contributes to various health benefits and why incorporating peppers into your diet can be a wise choice for overall wellness.
What is Capsaicin?
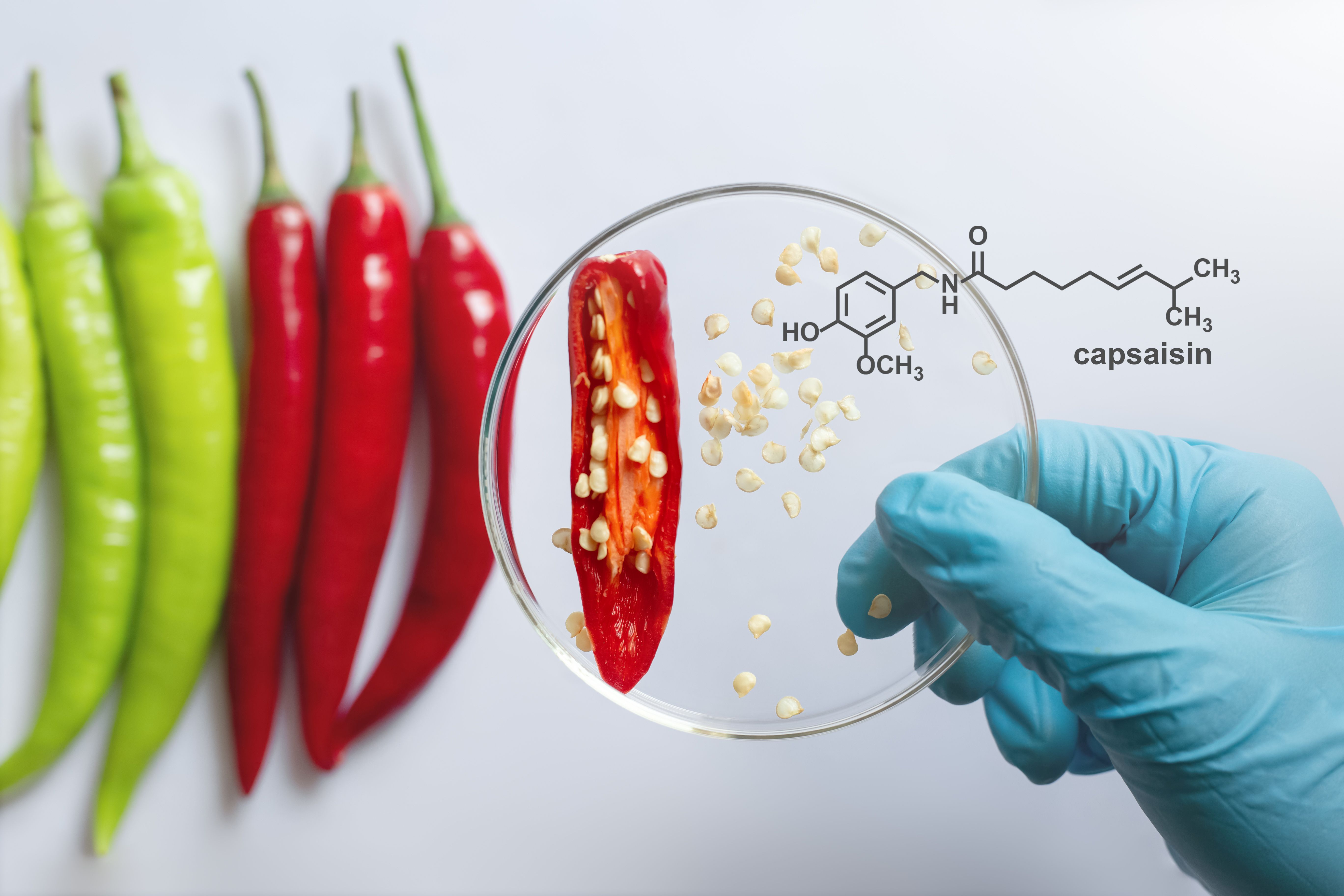

Capsaicin is the chemical compound responsible for the spicy heat in peppers. It primarily resides in the white pith and seeds of the fruit, and its concentration varies among different pepper varieties. The Scoville scale measures the heat level of peppers, with hotter peppers containing higher capsaicin levels.
Health Benefits of Capsaicin
1. Pain Relief
Mechanism
Capsaicin is known for its analgesic properties. It works by binding to pain receptors in the skin, which can lead to a temporary sensation of burning pain followed by a reduction in pain perception.
Applications
- Topical Treatments: Capsaicin creams and patches are often used to relieve pain from conditions like arthritis, neuropathy, and muscle strains.
- Chronic Pain Management: Regular use of capsaicin can desensitize pain receptors, offering long-term relief for chronic pain sufferers.
2. Metabolism Boost
Mechanism
Capsaicin has been shown to increase metabolic rate and promote fat oxidation. This thermogenic effect can help burn more calories, making it a popular ingredient in weight loss supplements.
Applications
- Weight Management: Including capsaicin-rich foods in your diet may aid in weight loss efforts by enhancing calorie expenditure and reducing appetite.
- Exercise Performance: Some studies suggest that capsaicin can improve exercise performance by increasing energy expenditure during workouts.
3. Cardiovascular Health
Mechanism
Capsaicin may contribute to heart health by improving circulation and reducing blood pressure. It has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Applications
- Cholesterol Levels: Regular consumption of capsaicin may help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels while increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Capsaicin can promote vasodilation, leading to improved blood flow and lower blood pressure.
4. Immune System Support
Mechanism
Capsaicin possesses antioxidant properties, which can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. This can enhance the immune response and overall health.
Applications
- Cold and Flu Prevention: The anti-inflammatory effects of capsaicin can help alleviate symptoms of respiratory infections and boost immunity.
- Digestive Health: Capsaicin can stimulate the production of digestive juices, promoting gut health and aiding in nutrient absorption.
5. Cancer Prevention
Mechanism
Some studies suggest that capsaicin may have anticancer properties due to its ability to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth.
Applications
- Research Findings: Preliminary research indicates that capsaicin may be effective against certain types of cancer, including prostate and colorectal cancer.
- Dietary Inclusion: While more research is needed, incorporating capsaicin-rich foods into a balanced diet may contribute to cancer prevention strategies.
How to Incorporate Peppers into Your Diet
To reap the health benefits of capsaicin, consider these practical ways to include peppers in your meals:
1. Fresh Salads
Add sliced or diced peppers to salads for a crunchy texture and vibrant color. Bell peppers, jalapeños, and other varieties can enhance both flavor and nutrition.
2. Salsas and Dips
Prepare fresh salsa using tomatoes, onions, cilantro, and chopped peppers. This can be a delicious and healthy dip for chips or a topping for tacos and grilled meats.
3. Stir-Fries and Curries
Incorporate peppers into stir-fries and curries for added spice and flavor. They pair well with a variety of proteins and vegetables.
4. Soups and Stews
Add chopped peppers to soups and stews for a boost of flavor and nutrients. They can enhance the overall taste and provide additional health benefits.
5. Pickled Peppers
Pickling peppers can preserve their flavor and heat while adding a tangy kick to sandwiches, salads, and charcuterie boards.
Potential Health Risks and Considerations
While capsaicin is generally safe for most people, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Digestive Discomfort: Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as heartburn or stomach upset, after consuming spicy foods. Moderation is key.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some people may be allergic to peppers or capsaicin. If you experience any adverse reactions, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional.
- Medication Interactions: Capsaicin may interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners. Consult your doctor if you have concerns about potential interactions.
Conclusion
Peppers, particularly those rich in capsaicin, offer numerous health benefits, from pain relief and metabolism boosting to cardiovascular support and immune enhancement. By incorporating peppers into your diet, you can enjoy their delicious flavor while reaping their health rewards.
Understanding Peppers Knowledge allows you to appreciate the nutritional value of this versatile vegetable. Whether enjoyed fresh, cooked, or pickled, peppers can be a valuable addition to a healthy lifestyle. Embrace the heat and flavor of peppers to enhance your health today!
Read Also About Pears are a delicious and refreshing fruit that offers a wide range of health benefits. Rich in fiber, vitamins C and K, potassium, and antioxidants, pears support heart health, aid digestion, and boost immunity.